Technical File on HRV
1. What Is HRV?
HRV stands for heart rate variability which is the physiological phenomenon of variation in the time interval between heartbeats. SA node generates an electrical signal that causes heart chambers to contract. In the meanwhile, the autonomic nervous system [ANS] is influenced by stressful circumstance, disease, or body status. This influenced ANS also has an effect on the heart beats and make them irregular. These irregular heartbeats are called HRV.
HRV is an indicator of body response coping with the circumstance changes. If HRV is analyzed, autonomic nervous system function, mental & physical stress, and physiological & psychological body status can be also indicated.
2. How to Obtain HRV Signals
Using ‘RR Interval’ on ECG, each distance between the heart beat can be indicated as a graph.
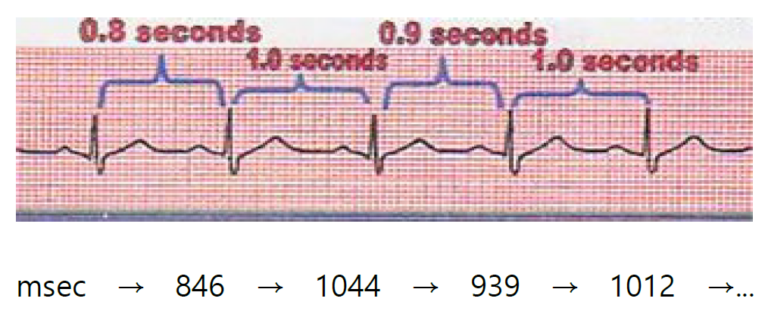
If you look at the ECG above, there are peak points. Each distance between the points are called ‘RR Interval’. This distance varies usually around 800msec. We vertically indicate each distance and link each point to obtain data as a graph. This valuable graph is HRV tachogram.
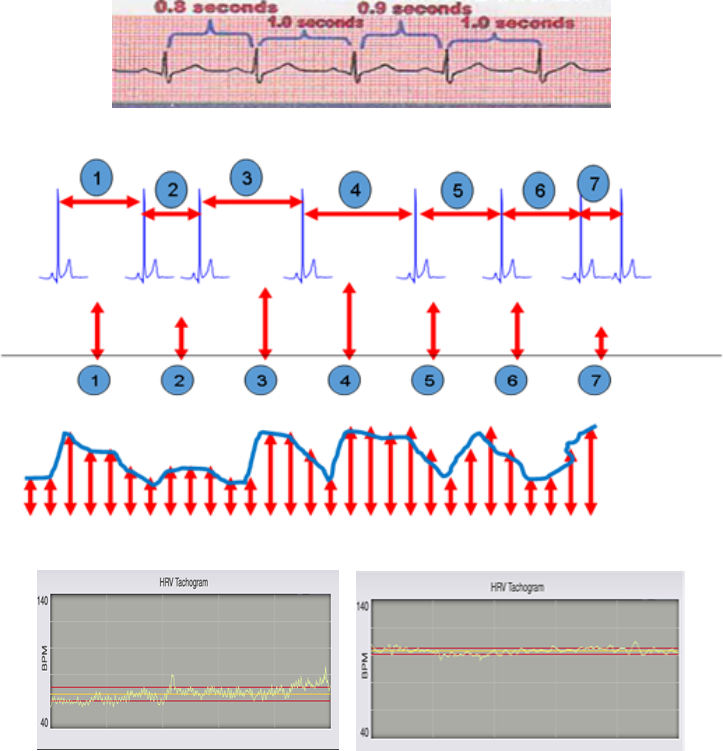
If the HRV graph has a dynamic fluctuation, the current HRV status is good and healthy. However, if it is flat and has less variation, this means that the HRV status is not good and unhealthy.
3. Benefits of HRV Measurement
– Non-invasive and safe
– Quantitative analysis on the activity and balance of autonomic nervous system
– Simultaneous analysis of sympathetic and parasympathetic nerve activity
– Prediction of overall health status
– Evaluation of physiological response to stress
– Evaluation of acute & chronic stress status
– Evaluation of physical & mental stress status
– Evaluation of the risk of stress-related diseases
– Evaluation of fatigue level
– Evaluation of electro cardiac stability
– Interpretation of digestive disorders
– Comparison of pre & post treatment
– Multipurpose usage with various therapy (IVNT, therapeutic exercise, respiratory, music, light, and, aroma therapy)
4. Autonomic Nervous System
The autonomic nervous system [ANS] is a division of the nervous system that operates internal organs, smooth muscle and glands. The autonomic nervous system is a control system that regulate heart rate, blood pressure, digestion, appetite, pupils and other body functions.
In the past, it was hard to objectively measure the autonomic nervous system. Now, it can be measured and used as an indicator of sympathetic nervous system [SNS] and parasympathetic nervous system [PNS] through time domain and frequency domain analysis.
ANS influences heart beats and make them irregular. These irregular heartbeats are called heart rate variability [HRV]. Therefore, measurement of HRV became a strong tool to evaluate the ANS function. Since HRV measurement is non-invasive, it only require very short time. HRV measurement is a reliable and safe method to obtain the physiological biofeedback.
1) Role of Autonomic Nervous System -> maintenance of homeostasis
Usually the sympathetic nervous system and parasympathetic nervous system have an antagonistic reaction to each other, and they remain in a balanced range. This phenomenon keeps body parts well balanced, control psychological process.
2) Sympathetic Nervous System
A function of the sympathetic nervous system is to stimulate the body’s fight or flight response which protects you from a stressful circumstance. A major role of the SNS is physiological processes such as body temperature, blood glucose levels, cardiac output, and immune system function. It is deeply related with homeostasis arisen from a circumstance change.
3) Parasympathetic Nervous System
A function of the parasympathetic nervous system is to stimulate ‘rest and digest’ or ‘feed and breed’ activities when the body is at rest. The PNS especially controls a maintenance of energy source, recovering and digestion (digestive system, and defecation)
4) Autonomic Nervous System and Stress
Stress can directly influence the autonomic nervous system that is related with physical and mental stress status. It especially makes the sympathetic nervous system dominant and reduce the response of the parasympathetic nervous system. In this way, the balance of homeostasis gets broken and it causes various diseases.
